Mergeomics is a flexible and streamlined pipeline that is able to retrieve meaningful biological insight from multiple types of omics data using multiple levels of analysis. Users can easily build their workflow based on their specific data and desired analysis. To facilitate one's analysis, we provide many different types of sample files including SNP to gene mapping, linkage disequilibrium files, and biological networks.
The two core functions of Mergeomics are marker set enrichment analysis (MSEA) and key driver analysis (KDA). Depending on the 7data type, there are slightly different considerations for MSEA, and so we have segmented the tutorial based on the specific data from the user. From MSEA to KDA, biological markers from significant marker sets found in MSEA and a network is input into KDA. The user can also run KDA as a first step using a list of markers (i.e genes) (tutorial in 'List(s) of genes' button below).
Sample input files can be found here. Sample outputs can be found here.
In addition to this tutorial, we have also embedded instructions throughout the pipeline workflow itself. Look for this button:
**Please save your session ID which can be copied by clicking on it at the top of the left sidebar so that you may return to your session at a later time or we recommend to enter your email when prompted to receive session information and results! (valid for 48 hours)
For an in-depth tutorial on how one can use Mergeomics, click below on the data type you have.
Preprocess data: marker dependency filtering (MDF).
|
1
|
Start pipeline. If you have a single GWAS study, click on 'Individual GWAS Enrichment'. A common preprocessing step of GWAS analysis is to correct for SNP dependencies based on linkage disequilibrium. We include marker dependency filtering (MDF) in our GWAS pipeline by default for this step which also maps SNPs to genes. You may skip this step in this workflow by clicking the "Skip MDF " button. |
|
|||||||||||||
|
2
|
Upload or select association file. A two column file is required with SNPs in the 'MARKER' column and association strength (e.g., -log10 transformed p-values, effect size, etc.) in the 'VALUE' column. Many different GWAS sample files are provided including metabolic, neurological, and psychiatric disorders. When uploading a GWAS file, upload all associations including those that do not reach nominal significance. |
File format
Example sample files provided
|
|||||||||||||
|
3
|
Upload or select SNP to gene mapping file. SNPs in 'MARKER' column and mappped genes in 'GENE' column (i.e., using eQTLs, distance-based, etc.) |
File format
Example sample files provided
|
|||||||||||||
|
4
|
Upload or select linkage disequilibrium file. A three column file is needed with SNPs in 'MARKERa' and 'MARKERb' columns and the correlation value in the 'WEIGHT' column. We provide 1000 Genomes linkage disequilibrium files from all 26 populations as sample linkage files. An example of a sample choice is "CEU LD50". LD50 means that it will filter out SNPs with a correlation of 50% or higher. The three letter code refers to the population which can be decoded here. |
File format
Example sample files provided
|
|||||||||||||
|
5
|
Choose top percentage of associations. Adjust accordingly based on the size of your GWAS. For example, try using 100 for small GWAS studies and 20 for large GWAS studies. |

|
|||||||||||||
|
6
|
Review files and submit MDF job. Click 'Click to Review' to see files and parameters chosen. Enter an email and click 'Send Email' to receive emails when the job starts and when the job ends with a link to return to your session to continue onto MSEA. Check the spam folder if the email is missing. Then click 'Run MDF Pipeline' to submit the job. Depending on the size of the inputs, the analysis can range from 5 minutes to 30 minutes. |

|
|
Run marker set enrichment analysis (MSEA) |
|
MSEA Results Interpretation
|
|
Merged Modules Results Interpretation
|
|
13
|
Choose to run wKDA or PharmOmics analysis (optional). Users can stop their analysis at MSEA or continue to wKDA (go to step 14) or PharmOmics (go to step 20) if there are significant results from MSEA (FDR less than 0.05 or 0.25 are the recommended significance levels). User can choose one route and still run the other by opening the MSEA toggle and clicking on the other analysis. |

|
|
Run MSEA to key driver analysis (KDA) |
|
14
|
Select/upload network file. The network file describes molecular connections. In a directed network, the source is in the 'HEAD' column and the target is in the 'TAIL' column. The network need not be directed or have weights (the 'WEIGHT' column can have all '1's). |
File format
Example sample files provided
|
|||||||||||||||
|
15
|
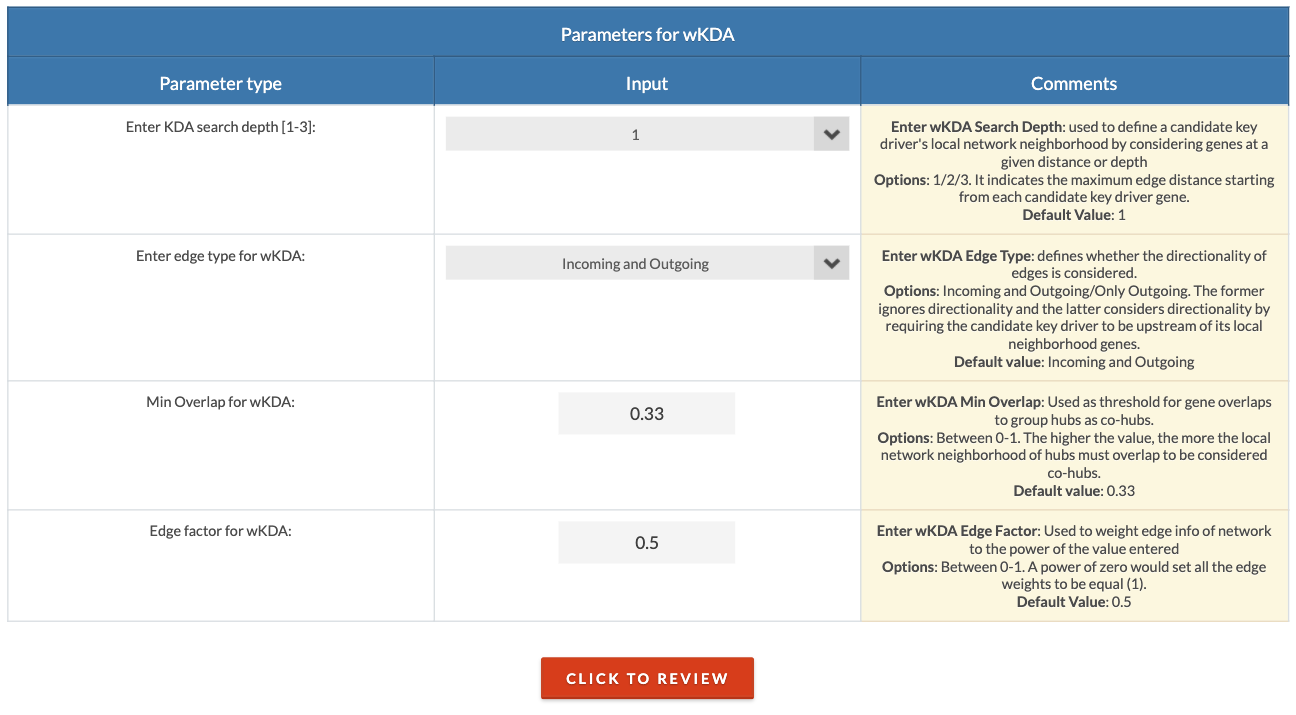
Choose KDA parameters. The search depth defines the distance (number of connections) away from a potential key driver that will be considered its local network neighborhood. A search depth of 1 is recommended but can be increased for sparse networks or small input gene lists. The edge type can be either 'Undirected' or 'Directed'; the former means that directionality (source and target designation) is not considered, and the latter means it is considered. The min overlap is the threshold above which hubs will be designated as co-hubs. The edge factor is the degree of influence of a edge weight. 0 is no influence (all weights are equal), 0.5 is partial influence, and 1 is full influence. |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
16
|
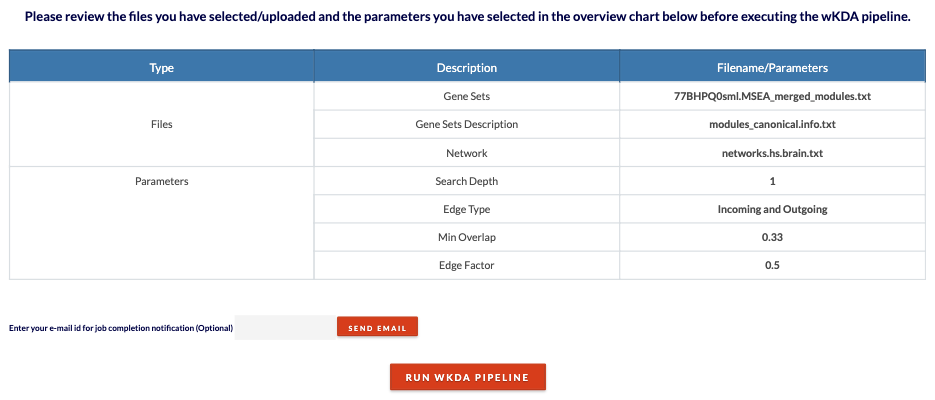
Review KDA files/parameters and submit job. Click 'Click to Review' to see files and parameters chosen. Click 'Run wKDA Pipeline' to submit the job. Depending on the size of the inputs, the analysis can range from 10 minutes to 2 hours. |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
17
|
Retrieve KDA results. At the conclusion of KDA, key driver results files and cytoscape files are generated. The 'Key Drivers Results' file lists for each key driver its P and FDR values, the module of which it is a key driver for, the total number of neighbors ('N.neigh'), the number of neighbors that are members of the module ('N.obsrv'), and the expected (null) number of neighbors that are members of the module as calculated by permutation. The cytoscape files can be used on Cytoscape Desktop for the user to customize the network visualization. Cytoscape visualization of the top 5 key drivers for each module can be viewed on the browser by clicking on 'Display KDA subnetwork'. The analysis can be concluded at this step or subnetwork genes can be used for drug repositioning in the PharmOmics pipeline by clicking on 'Run PharmOmics pipeline'. In the case that no significant (FDR < 0.05) key drivers are found, cytoscape files will not be generated. However, an option to view module gene overlap (if any) with network genes will appear. |
|
|
KDA Results Interpretation
|
|
Run KDA to PharmOmics |
|
18
|
(Optional) Select inputs for KDA to PharmOmics analysis. The user can conclude analysis at KDA or run drug based repositioning on KDA subnetwork results. Choose to run overlap based drug repositioning (around 5 min to run) or network based drug repositioning (around 30 minutes to 2 hours to run). Next, choose all genes from the generated subnetwork, only genes from input modules (i.e. gene sets) in the subnetwork (not including subnetwork genes that are not members of input modules), or the user can choose specific modules to include. For drug network repositioning, you additionally need to select or upload a network and select the species. Also for network drug repositioning, we offer only the option to query meta signatures (studies using different dose and treatment durations are meta-analyzed). You may use your results in our separate PharmOmics pipeline to run the dose/time segregated analysis which will take around 3 hours to complete and will require a login due to heavy use of computational resources. |

|
|
19a
|
Retrieve PharmOmics results from overlap based drug repositioning. Image on the right shows results from the overlap based drug repositioning option. The results ranks the drugs based on concordance between the KDA subnetwork genes and the drug signatures genes (Jaccard score). Data from our comprehensive species- and tissue-specific drug signatures are used as well as L1000 signatures. The drug repositioning results and the genes used for repositioning can be obtained from the download links. |
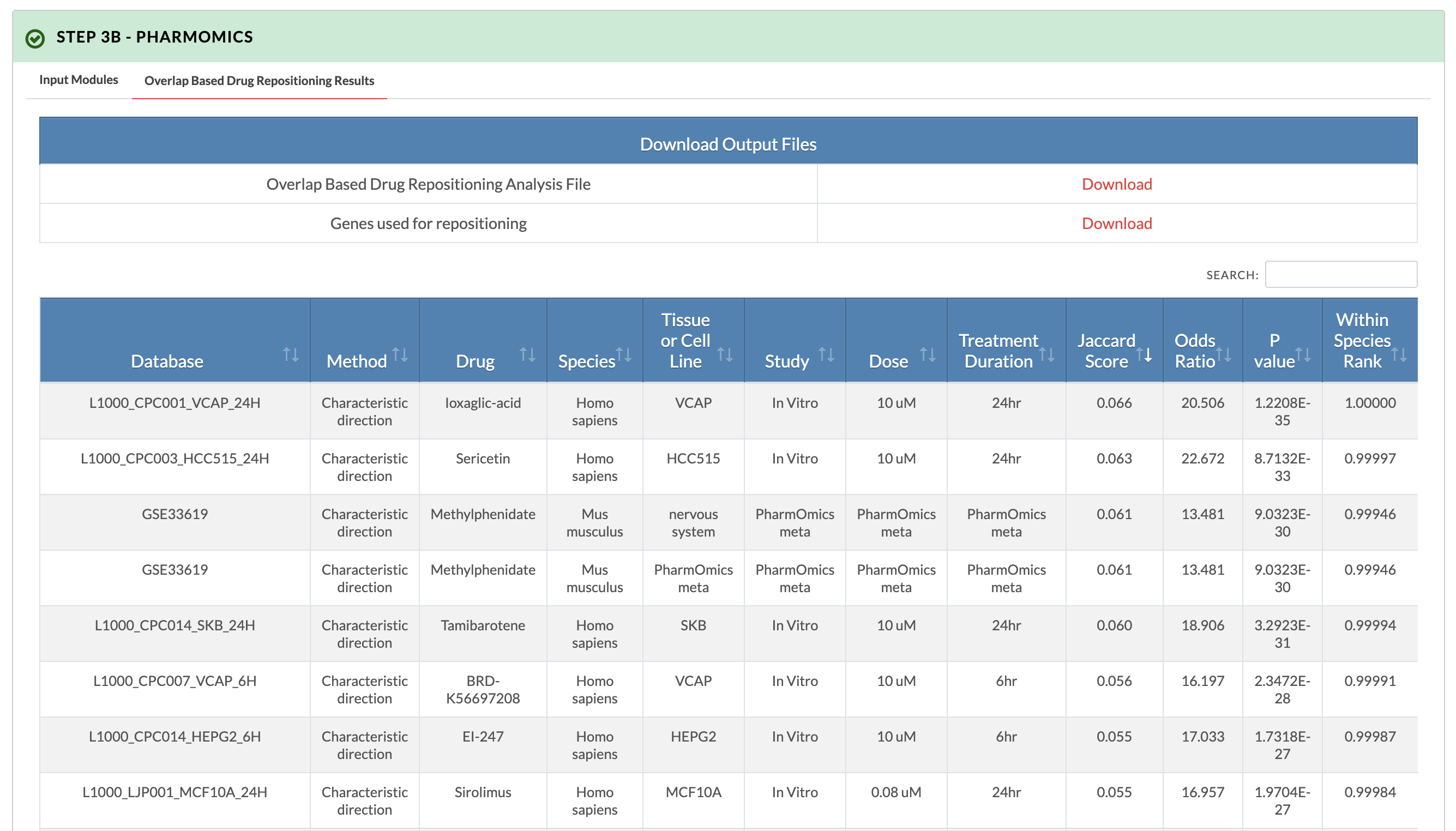
|
|
19b
|
Retrieve PharmOmics results from network based drug repositioning. Image on the right shows results from the network based drug repositioning option. The results ranks the drugs based on the significance of connectivity between drug signature genes and input genes as defined by a gene network model. Signatures from our comprehensive species- and tissue-specific drug signatures database are used. The drug repositioning results and the genes used for repositioning can be obtained from the download links. We also provide links to visualize the network model of drug genes and their first neighbor input genes (input genes having one edge distance from drug gene). |
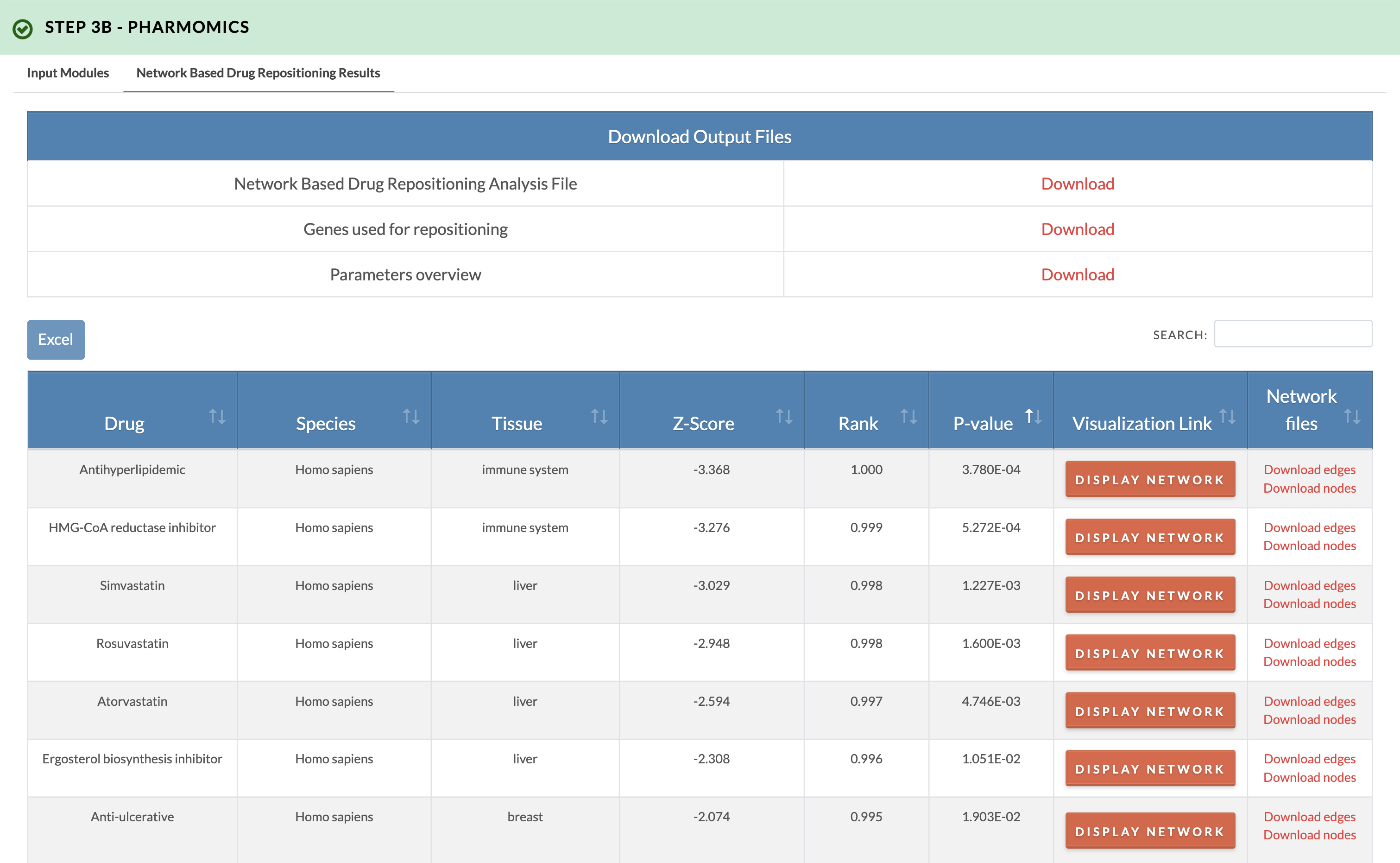
|
|
Run MSEA to PharmOmics |
|
20
|
Select input modules and drug repositioning type. Choose to run overlap (around 5 min to run) or network based drug repositioning (around 30 minutes to 2 hours to run). Next, choose to run all modules below a specified significance threshold or select specific modules. Finally, choose whether to use genes from the entire geneset or only those genes that were mapped from SNPs (genes derived from association data). For drug network repositioning, you additionally need to select or upload a network and select the species. Also for network drug repositioning, we offer only the option to query meta signatures (studies using different dose and treatment durations are meta-analyzed). You may use your results in our separate PharmOmics pipeline to run the dose/time segregated analysis which will take around 3 hours to complete and will require a login due to heavy use of computational resources. Please refer to steps 19a and 19b to read interpretation of PharmOmics results. |
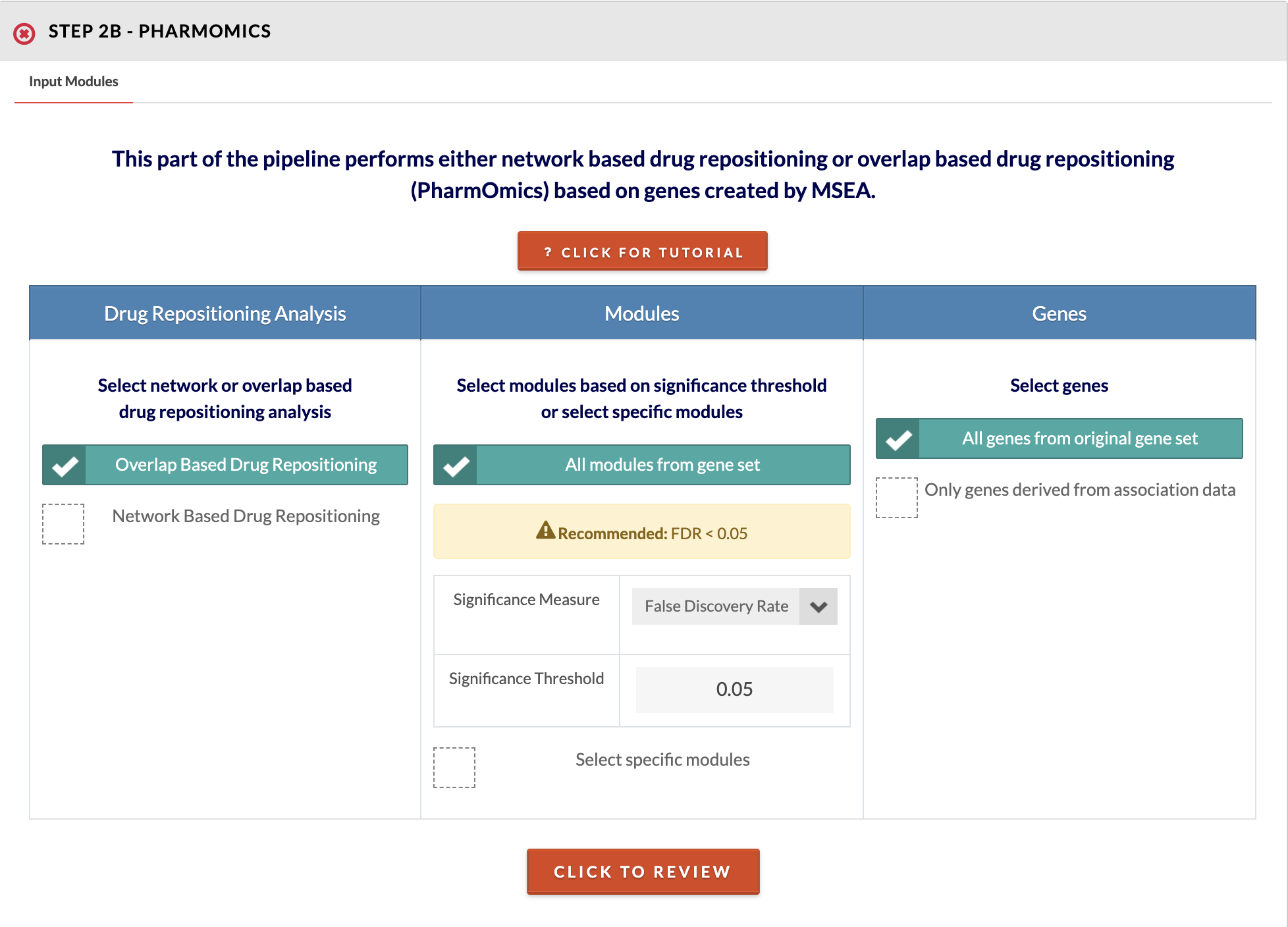
|
The workflow for epigenome-, transcriptome-, proteome-, and metabolome-wide association studies is similar to GWAS except that it does not include a mapping file or marker dependency filtering by default though it is included as optional steps in this pipeline. This is because TWAS and PWAS markers do not need to be mapped to genes (if gene sets are to be tested). However, we leave the options to include a mapping file and run marker dependency filtering as epigenome markers such as CpG sites may be mapped to genes and also may have dependencies. Currently, we do not provide any metabolite marker sets or metabolite to gene mapping files, but the user can provide these files.
Run marker set enrichment analysis (MSEA).
|
1
|
Start pipeline. If you have a single TWAS, EWAS, PWAS, or MWAS study, click on 'Individual EWAS, TWAS, PWAS, or MWAS enrichment' on the Run Mergeomics page. |
|
||||||||||||
|
2
|
Upload or select association file. A two column file is required with markers (i.e. genes, methylation sites, etc.) in the 'MARKER' column and association strength (e.g., -log10 transformed p-values, fold change, etc.) in the 'VALUE' column. You may first upload all associations including those that do not reach nominal significance and adjust the cutoff of signals to include accordingly (top 50%, 20%, etc.). |
File format
Example sample files provided
|
||||||||||||
|
3
|
(Optional) Upload/select mapping file. If your markers do not match those of the marker sets to be enriched, then select 'Yes' to the question 'Would you like to use a mapping file?' and upload or select a mapping file. For example, we provide CG methylation probe ID to gene mappings and gene sets can subsequently be tested for enrichment. Transcriptome and proteome data usually do not require a mapping file. The required file format is pictured to the right ('MARKER' and 'GENE' columns). |
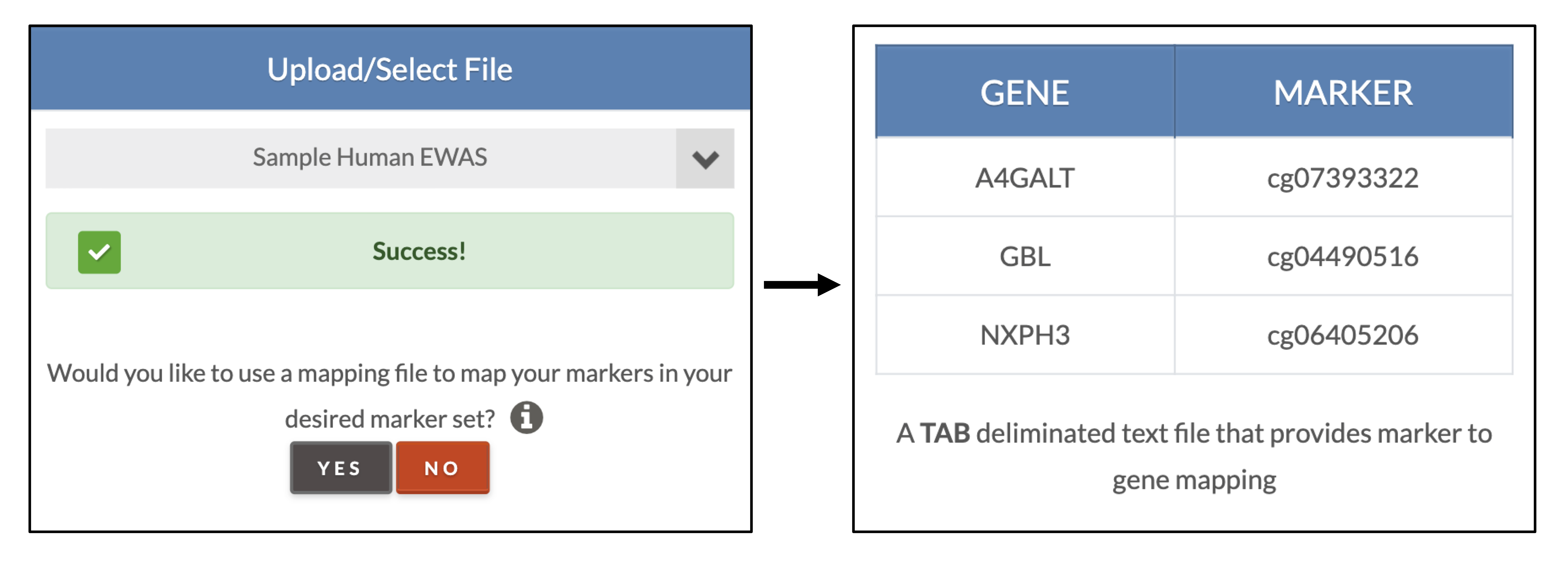
|
||||||||||||
|
4
|
(Optional) Upload marker dependency file. If there are dependencies between markers that may lead to spurious associations, a dependency file can be uploaded and if both constituents of any of the marker pairs in the dependency file is detected, the marker with the highest association value will be kept. This option only appears if a mapping file is used. |
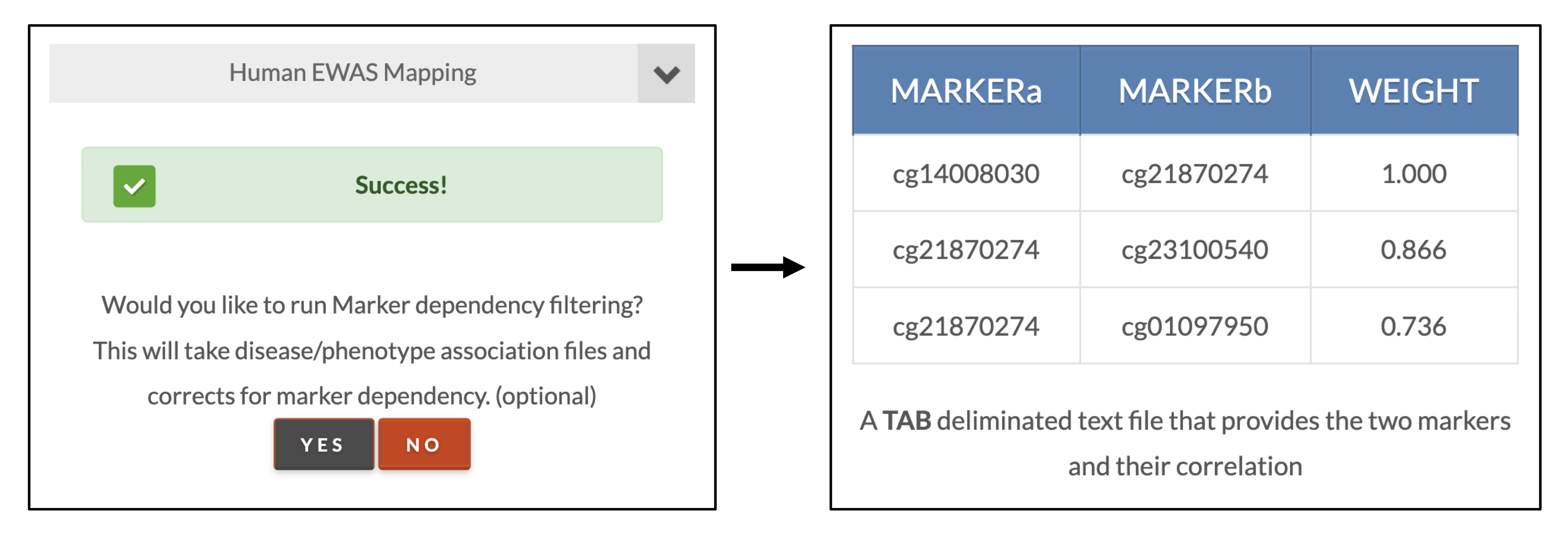
|
||||||||||||
|
5
|
Select/upload gene sets. These are the gene sets that will be tested for association to the disease. Gene sets can be knowledge-driven canonical pathways or data-driven coexpression modules. |
File format
Example sample files provided
|
||||||||||||
|
6
|
(Optional) Select/upload gene sets descriptions. An optional file to include in order to annotate modules in results files. The DESCR column has a full description of the MODULE. Minimum columns needed are MODULE and DESCR. If a sample gene set is chosen, the descriptions will be added automatically. |
File format
|
||||||||||||
|
7
|
Choose MSEA parameters. Default parameters are recommended settings. A description of each parameter can be viewed upon clicking on the 'Click For Tutorial' button. For EWAS/TWAS/PWAS/MWAS data, the permutation type is set to "marker" and Max Overlap for Merging Gene Mapping is set to 1 (means no merging) (only applies to GWAS data). Min Module Overlap Allowed for Merging is the minimum overlap ratio for which a module will remain independent. Modules with overlap ratios above this value will be merged. Set to 1 to skip module merging. Number of Permutations: For formal analysis, 10,000 permutations should be used, and 2,000 can be set for exploratory analysis. MSEA to KDA export FDR cutoff: Modules with an FDR less than this cutoff will be used for key driver analysis (KDA). If no modules pass this significance, the top 10 pathways regardless of FDR will be export to KDA. The user must interpret the results accordingly. |
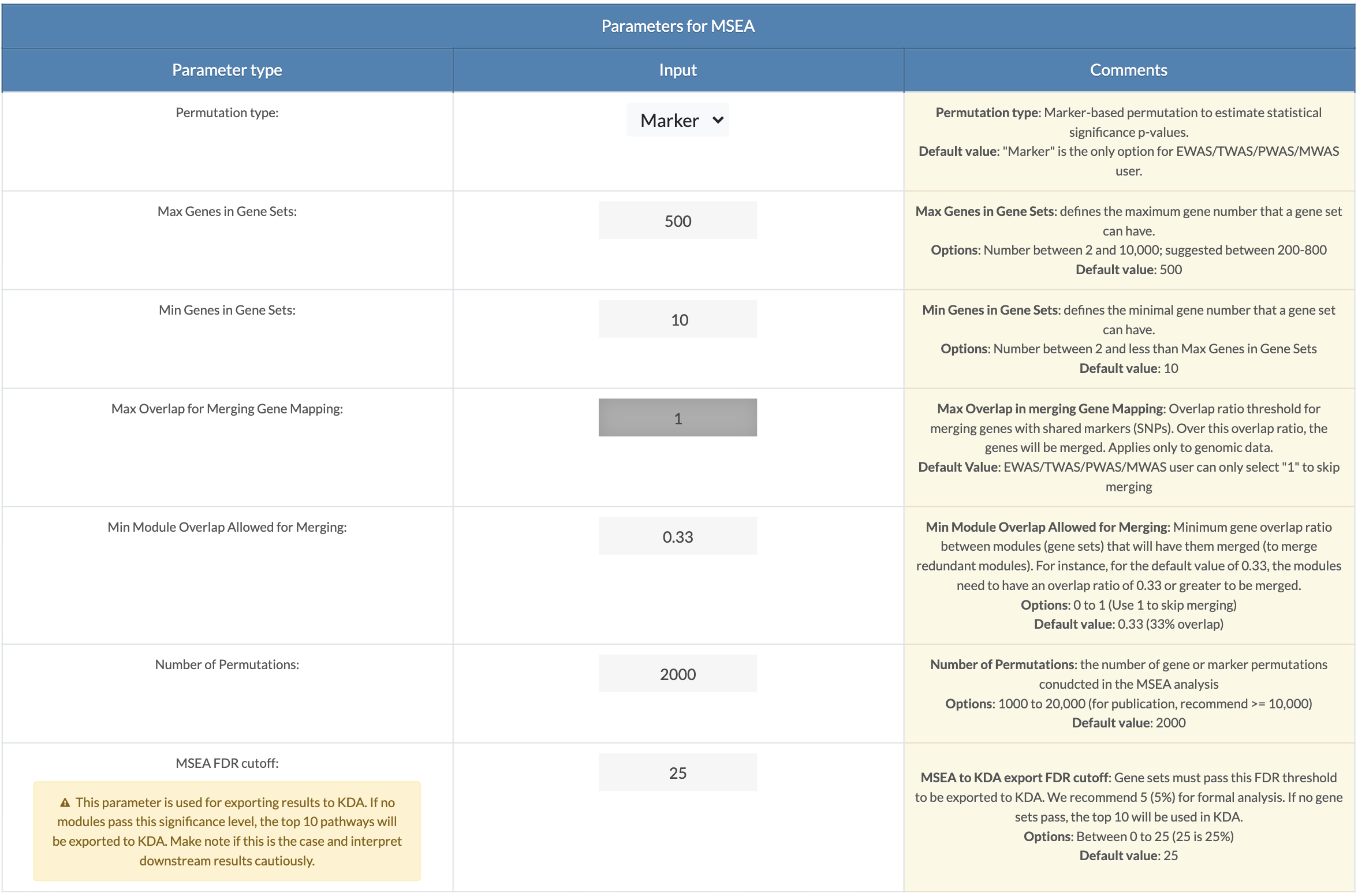
|
||||||||||||
|
8
|
Review files/parameters and submit MSEA job. Click 'Click to Review' to see files and parameters chosen. Click 'Run MSEA Pipeline' to submit the job. Depending on the size of the inputs and number of permutations, the analysis can range from 10 minutes to 2 hours. To speed up computation time, decrease the number of permutations. |
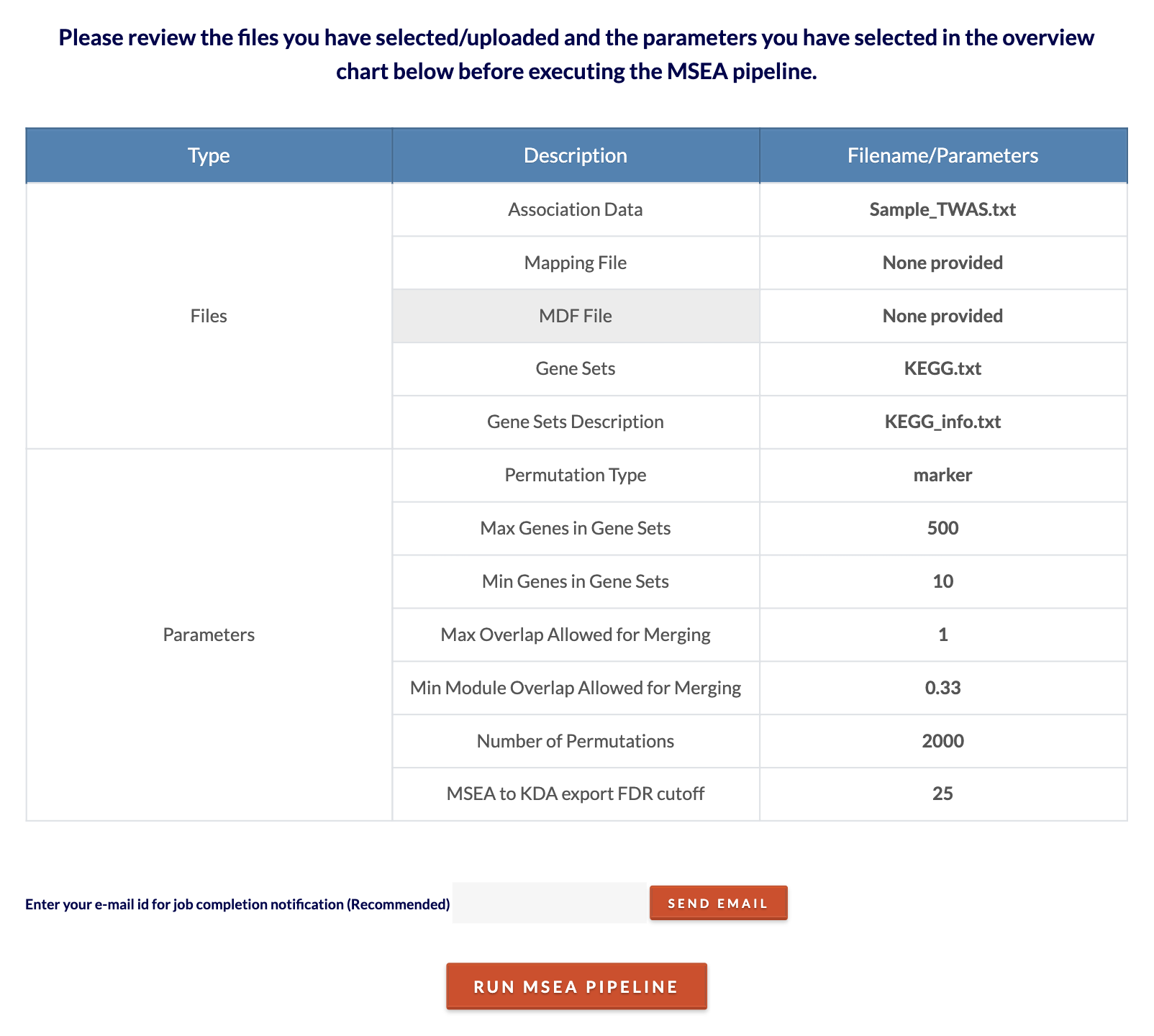
|
||||||||||||
|
9
|
Retrieve MSEA results. At the conclusion of MSEA, a download results table with appear and if an email address was entered, these results will also be emailed to that address. The Module Details file lists genes mapped from SNPs of the modules and the association strengths of the SNPs (as given in the association input file). The Modules Results Summary file reports module significance and number of genes and markers that contributed to the module. The Merged Modules Results Summary file is the full results for supersets (similar modules merged) and independent modules (not similar to any other modules). The Merged Modules Nodes for KDA file lists the nodes or gene sets that will be used for KDA. The website displays individual module results and merged modules results (pictured is the display of individual module results and users can toggle to the 'Merge Module Results'). Below is the interpretation of those tables. |
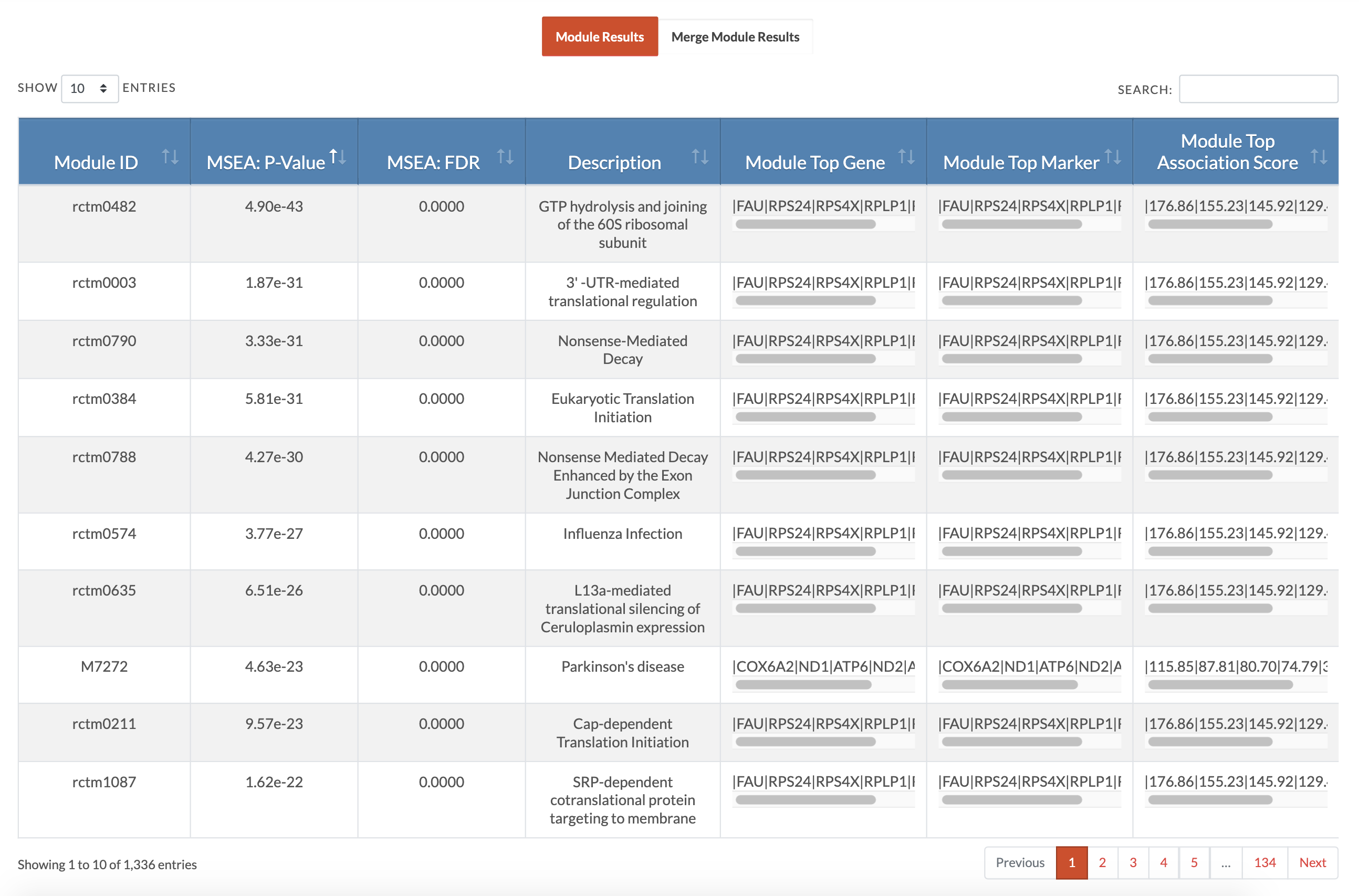
|
|
MSEA Results Interpretation
|
|
Merged Modules Results Interpretation
|
|
10
|
Choose to run wKDA or PharmOmics analysis (optional). Users can stop their analysis at MSEA or continue to wKDA (go to step 11) or PharmOmics (go to step 17) if there are significant results from MSEA (FDR less than 0.05 or 0.25 are the recommended significance levels). Users can choose one route and still run the other by opening the MSEA toggle and clicking on the other analysis. |

|
|
Run MSEA to key driver analysis (KDA) |
|
11
|
Select/upload network file. The network file describes molecular connections. In a directed network, the source is in the 'HEAD' column and the target is in the 'TAIL' column. The network need not be directed or have weights (the 'WEIGHT' column can have all '1's) |
File format
Example sample files provided
|
|||||||||||||||
|
12
|
Choose KDA parameters. The 'search depth' defines the distance (number of connections) away from a potential key driver that will be considers its local network neighborhood. A search depth of 1 is recommended but can be increased for sparse networks or small input gene lists. The 'edge type' can be either 'Undirected' or 'Directed'; the former means that directionality (source and target designation) is not considered and the latter means it is considered. The 'min overlap' is the threshold above which hubs will be designated as co-hubs. The 'Edge factor' is the degree of influence of a edge weight. 0 is no influence (all weights are equal), 1 is full influence, and 0.5 is partial influence. |

|
|||||||||||||||
|
13
|
Review KDA files/parameters and submit job. Click 'Click to Review' to see files and parameters chosen. Click 'Run wKDA Pipeline' to submit the job. Depending on the size of the inputs, the analysis can range from 10 minutes to 2 hours. |

|
|||||||||||||||
|
14
|
Retrieve KDA results. At the conclusion of KDA, key driver results files and cytoscape files are generated. The 'Key Drivers Results' file lists for each key driver its P and FDR values, the module of which it is a key driver for, the total number of neighbors ('N.neigh'), the number of neighbors that are members of the module ('N.obsrv'), and the expected (null) number of neighbors that are members of the module as calculated by permutation. The cytoscape files can be used on Cytoscape Desktop for the user to customize the network visualization. Cytoscape visualization of the top 5 key drivers for each module can be viewed on the browser by clicking on 'Display KDA subnetwork'. The analysis can be concluded at this step or subnetwork genes can be used for drug repositioning in the PharmOmics pipeline by clicking on 'Run PharmOmics pipeline'. |

|
|
KDA Results Interpretation
|
|
Run MSEA to PharmOmics |
|
15
|
(Optional) Select inputs for KDA to PharmOmics analysis. The user can conclude analysis at KDA or run drug based repositioning on KDA subnetwork results. Choose to run overlap based drug repositioning (around 5 minutes to run) or network based drug repositioning (around 30 minutes to 2 hours to run). Next, choose all genes from the generated subnetwork, only genes from input modules (i.e., gene sets) in the subnetwork (not including subnetwork genes that are not members of input modules), or the user can choose specific modules to include. For drug network repositioning, you additionally need to select or upload a network and select the species. Also for network drug repositioning, we offer only the option to query meta signatures (studies using different dose and treatment durations are meta-analyzed). You may use your results in our separate PharmOmics pipeline to run the dose/time segregated analysis which will take around 3 hours to complete and will require a login due to heavy use of computational resources. |

|
|
16a
|
Retrieve PharmOmics results from overlap based drug repositioning. Image on the right shows results from the overlap based drug repositioning option. The results ranks the drugs based on concordance between the KDA subnetwork genes and the drug signatures genes (Jaccard score). Data from our comprehensive species- and tissue-specific drug signatures are used as well as L1000 signatures. The drug repositioning results and the genes used for repositioning can be obtained from the download links. |
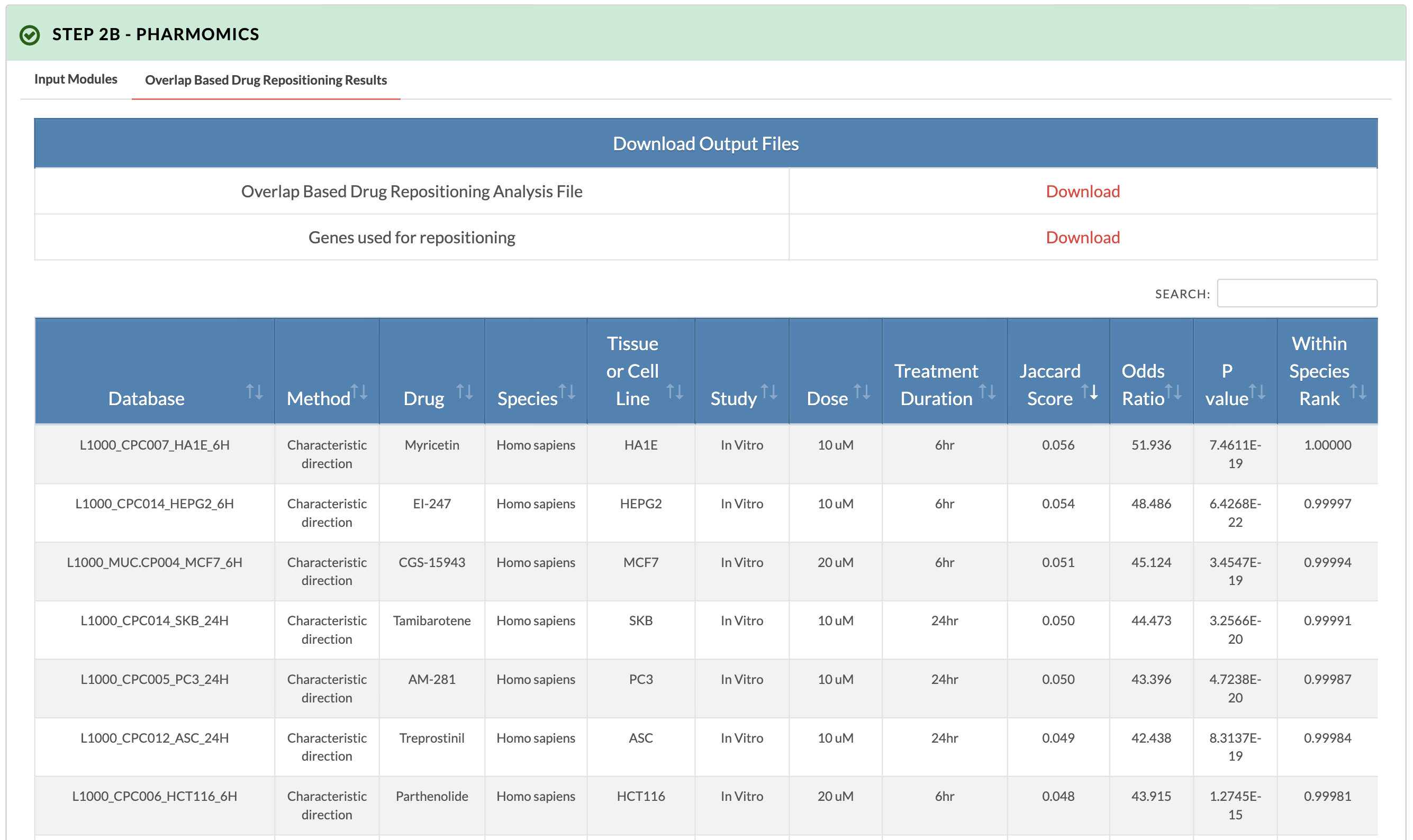
|
|
16b
|
Retrieve PharmOmics results from network based drug repositioning. Image on the right shows results from the network based drug repositioning option. The results ranks the drugs based on the significance of connectivity between drug signature genes and input genes as defined by a gene network model. Signatures from our comprehensive species- and tissue-specific drug signatures database are used. The drug repositioning results and the genes used for repositioning can be obtained from the download links. We also provide links to visualize the network model of drug genes and their first neighbor input genes (input genes having one edge distance from drug gene). |
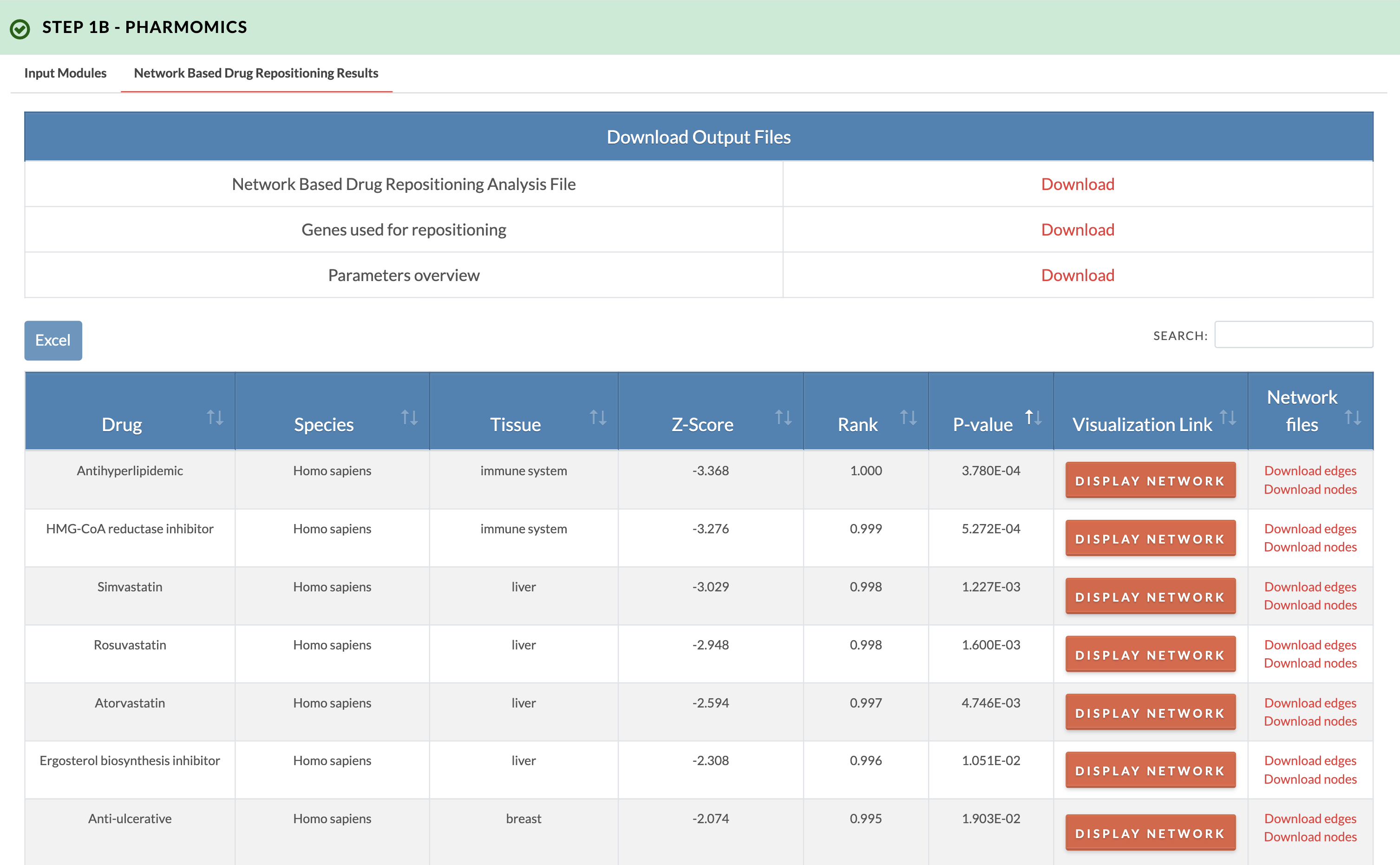
|
|
Run MSEA to PharmOmics |
|
17
|
Select input modules and drug repositioning type. Choose to run overlap (around 5 min to run) or network based drug repositioning (around 30 minutes to 2 hours to run). Next, choose to run all modules below a specified significance threshold or select specific modules. For drug network repositioning, you additionally need to select or upload a network and select the species. Also for network drug repositioning, we offer only the option to query meta signatures (studies using different dose and treatment durations are meta-analyzed). You may use your results in our separate PharmOmics pipeline to run the dose/time segregated analysis which will take around 3 hours to complete and will require a login due to heavy use of computational resources. Please refer to steps 16a and 16b to read interpretation of PharmOmics results. |

|
In meta-MSEA, a marker set level meta analysis is done for any combination of multiple omics studies (multiple of the same type or different types). MSEA is run separately on each dataset and a meta p-value is calculated across the datasets.
Add datasets and run meta-MSEA
|
1
|
Start pipeline. If you have multiple omics studies (multiple of the same type or multiple of different types) to analyze and would like to run a marker set level meta analysis, click on 'Multiple Omics Datasets (GWAS, EWAS, TWAS, PWAS, MWAS) enrichment'. |

|
|
2
|
Choose type of association data to add. According to your data type, select 'GWAS Enrichment' or 'EWAS/TWAS/PWAS/MWAS Enrichment'. This separation exists because the preprocessing of and parameters for GWAS and EWAS/TWAS/PWAS/MWAS data for MSEA are slightly different. |
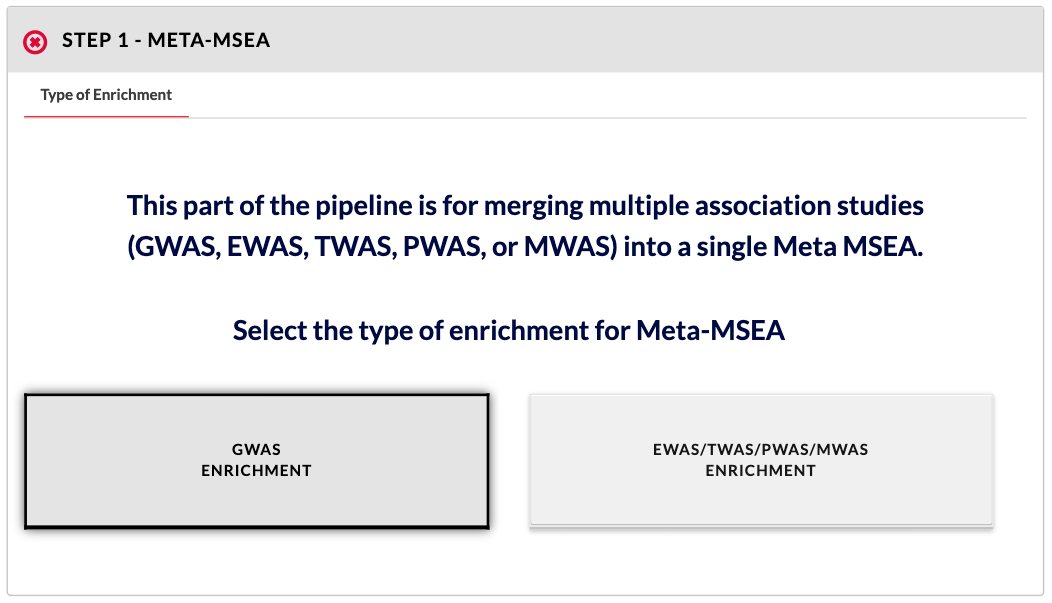
|
|
3
|
Select/upload files and parameters for MSEA for each dataset. The workflow for adding files and parameters for GWAS and EWAS/TWAS/PWAS/MWAS data is the same as in the individual pipelines. Refer to the 'Run marker set enrichment analysis section' for GWAS and for EWAS/TWAS/PWAS/MWAS. You may also refer to the 'Data input details' and 'Parameters details' sections below. |
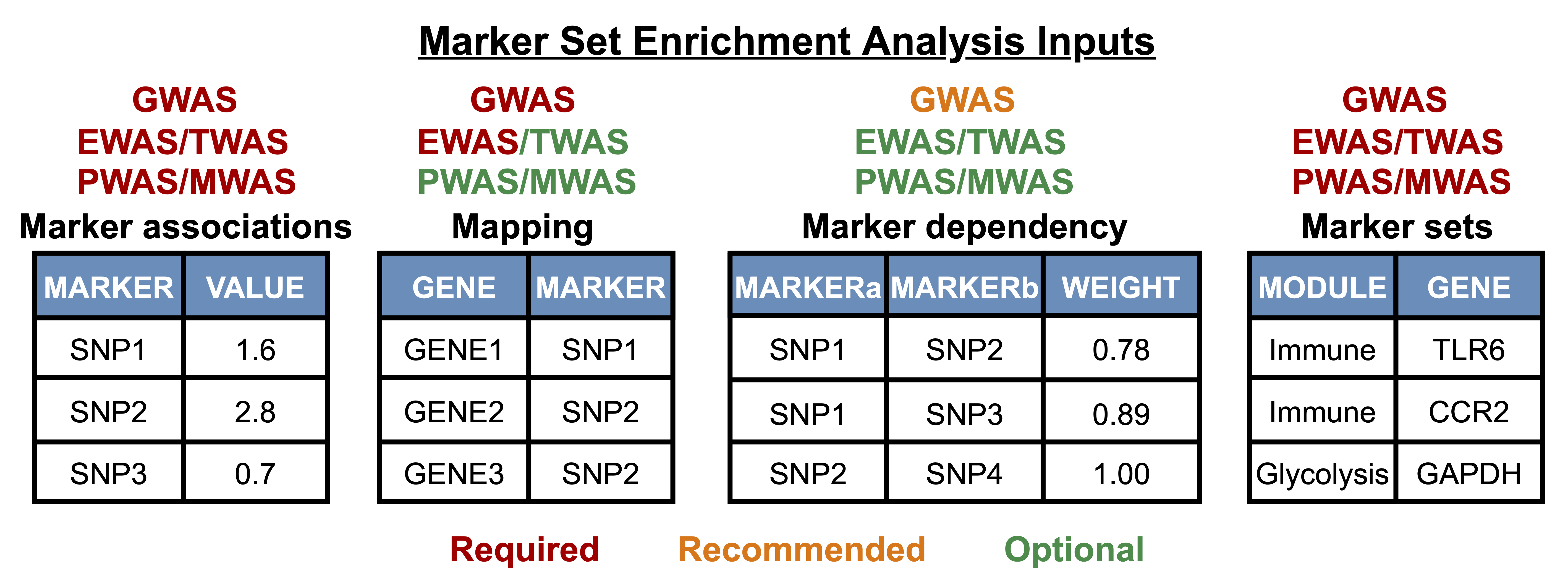
|
|
4
|
Select parameters for MSEA for each dataset. "Gene" permutation is recommended for GWAS and "Marker" is the only option for EWAS/TWAS/PWAS/MWAS. "Max Overlap for Merging Gene Mapping" is the overlap ratio threshold for merging genes with shared markers (SNPs). This applied only to GWAS data and is set to 1 for EWAS/TWAS/PWAS/MWAS data. The "MSEA to KDA export FDR cutoff" is the cutoff for the individual MSEA to be considered for KDA. Set the value to 100 to have no cutoff apply for the specific dataset. The module/gene set will still need to pass the Meta-MSEA FDR cutoff. |
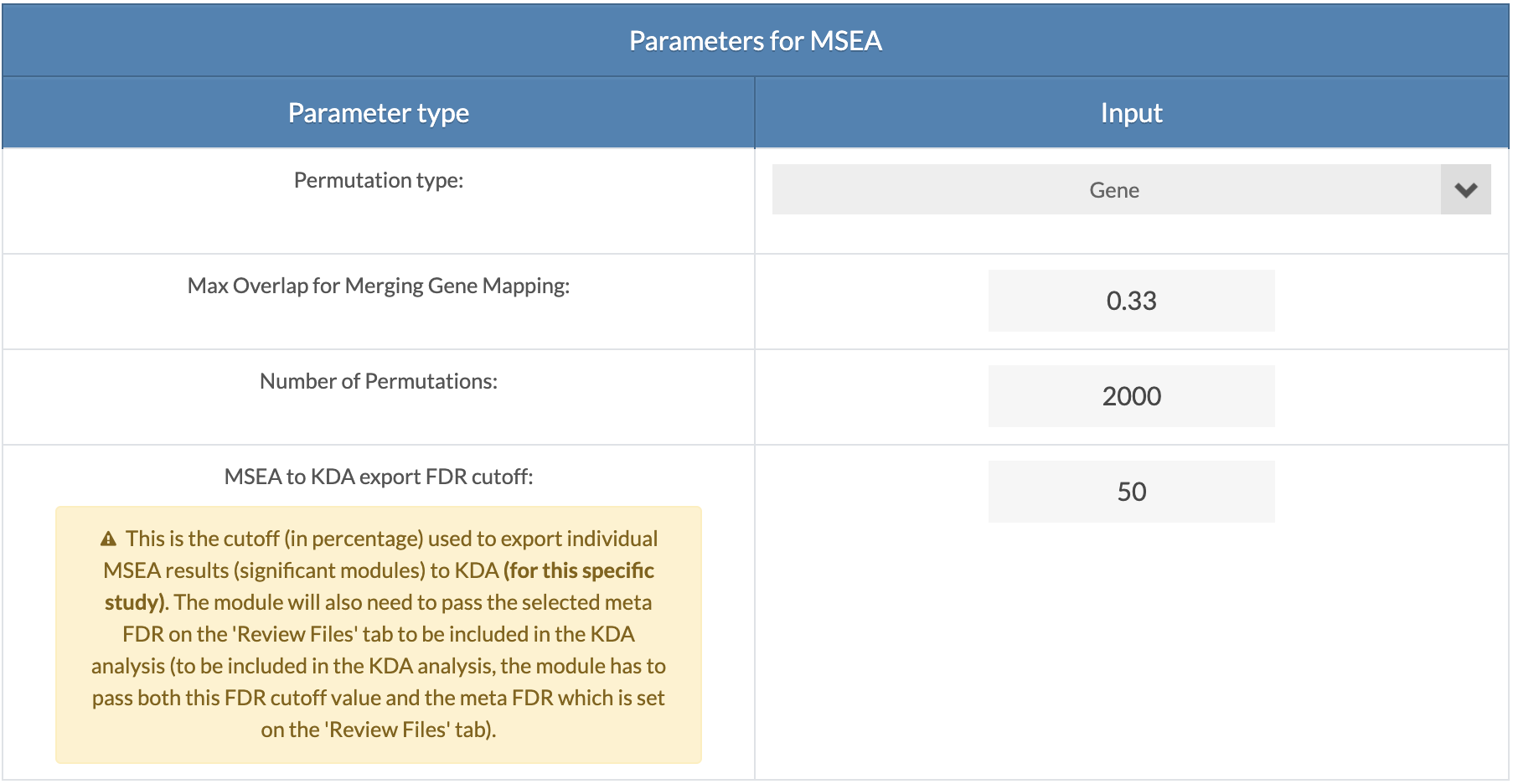
|
|
5
|
Review datasets. Each dataset addition with be appended to this review table. Added datasets can be deleted and more datasets can be added by clicking on 'Add another association data'. The minimum number of datasets is 2 and the maximum is 5. Because MSEA is run on mutiple datasets, the runtime may be very long (an individual MSEA run is usually 5 minutes to 30 minutes). Runtime can be shortened by decreasing number of permutations. |
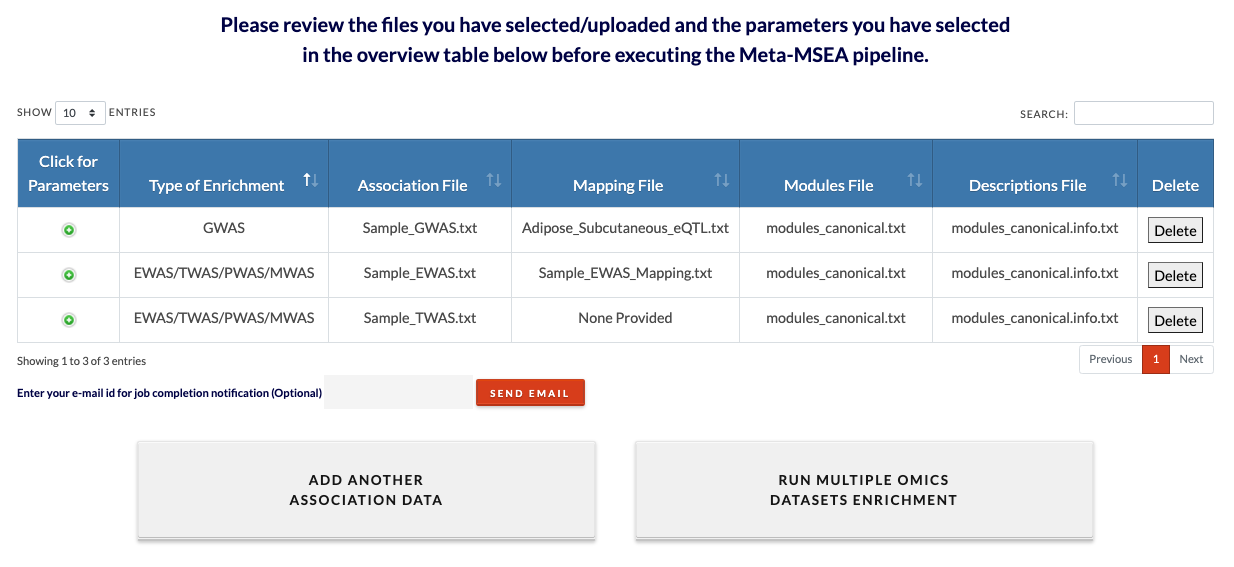
|
|
6
|
Select marker sets and parameters for Meta-MSEA.. "Min Module Overlap Allowed for Merging" is the minimum gene overlap ratio between modules that will have them merged (to merge redundant modules). We recommend the default value. "MSEA to KDA export Meta FDR cutoff" is the meta FDR cutoff to consider modules/gene sets for KDA. The modules must pass all individual MSEA cutoffs as well as the meta FDR cutoff to be included in KDA. To run meta-MSEA, click on 'Run multiple omics datasets enrichment'. |
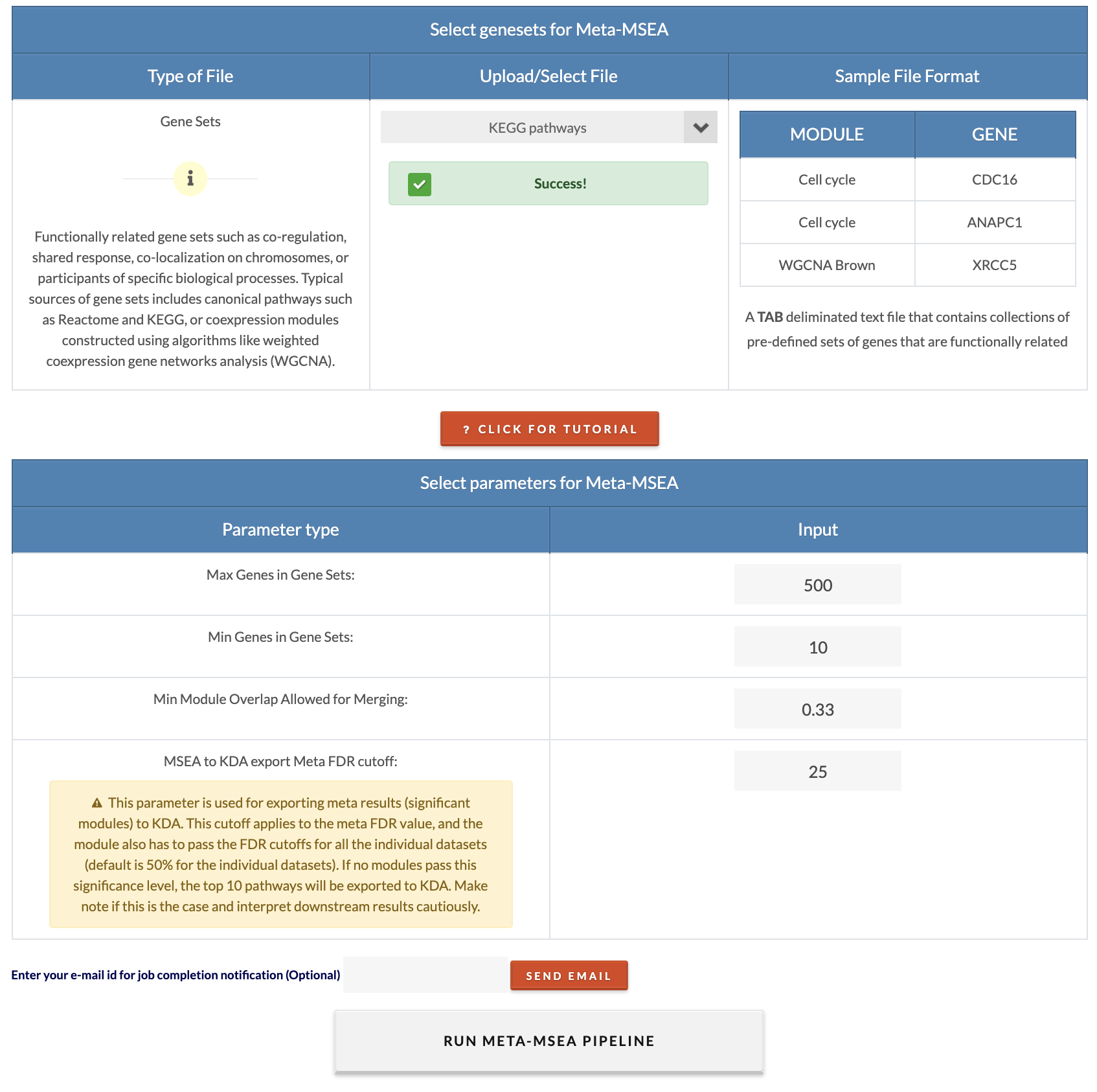
|
|
7
|
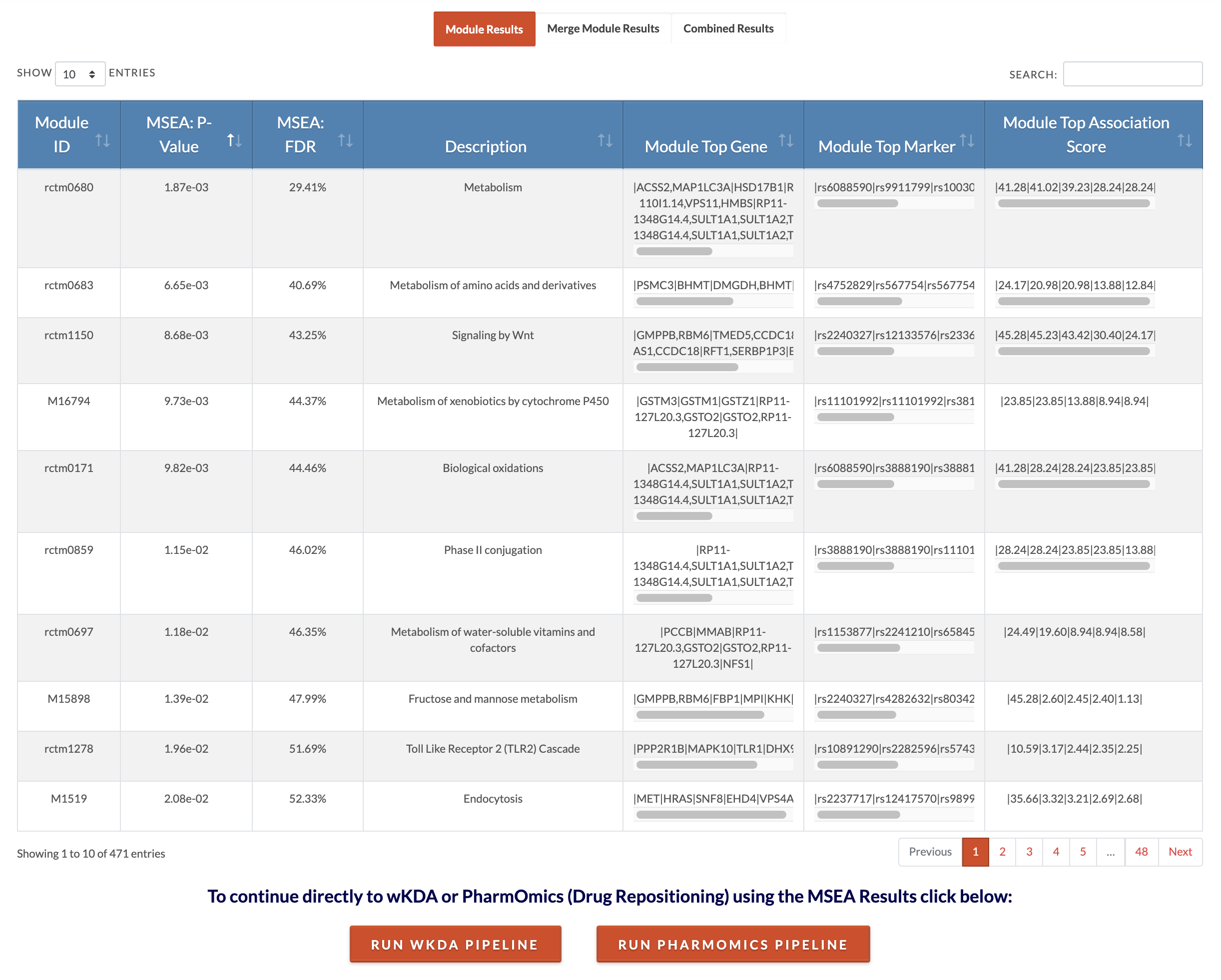
Retrieve meta-MSEA results. Result files available for download include the 'Modules Details' file which lists the genes that contributed to the module's association, the 'Full Results File' which lists for each module the P and FDR values of association significance and the number of genes that contributed to the module's association. The 'Merged Modules Full Results' file shows the results for nonredundant sets (similar gene sets are merged based on 'Min Module Overlap Allowed for Merging' parameter). The 'Merged Modules' file contains the genes that will be used as input to KDA if the user would like to run wKDA directly using the 'Run wKDA Pipeline' button. The 'Meta MSEA Individual Study P and FDR Results' file lists for each individual MSEA the association P and FDR values. Each dataset has an ID which can be decoded with the "Meta MSEA File and Parameter Selection" File. The 'Individual MSEA Result Files' is a zip file containing full MSEA results for each study. Interpretation for the interactive result tables is below. You may conclude your analysis at MSEA or continue to KDA (step 6). Please note that the default meta FDR cut off for associated modules from meta-MSEA is 25% (MSEA to KDA export FDR cutoff parameter). If you would like to be more stringent or lenient in your inclusion of modules, you may either edit the 'Merged Modules' file to only include your desired modules according to the significance results and use them in the standalone wKDA pipeline or rerun the analysis with a more stringent cutoff. PharmOmics can also be run on results from MSEA by clicking on 'Run PharmOmics Pipeline' (go to step 14). |
|
|
MSEA Results Interpretation
|
|
Merged Modules Results Interpretation
|
|
Combined Results Interpretation
|
|
Run Meta-MSEA to key driver analysis (KDA) |
|
8
|
Select/upload network file. The network file describes molecular connections. In a directed network, the source is in the 'HEAD' column and the target is in the 'TAIL' column. The network need not be directed or have weights (the 'WEIGHT' column can have all '1's) |
File format
Example sample files provided
|
|||||||||||||||
|
9
|
Choose KDA parameters. The 'search depth' defines the distance (number of connections) away from a potential key driver that will be considers its local network neighborhood. A search depth of 1 is recommended but can be increased for sparse networks or small input gene lists. The 'edge type' can be either 'Undirected' or 'Directed'; the former means that directionality (source and target designation) is not considered and the latter means it is considered. The 'min overlap' is the threshold above which hubs will be designated as co-hubs. The 'Edge factor' is the degree of influence of a edge weight. 0 is no influence (all weights are equal) and 1 is full influence. |

|
|||||||||||||||
|
10
|
Review KDA files/parameters and submit job. Click 'Click to Review' to see files and parameters chosen. Click 'Run wKDA Pipeline' to submit the job. Depending on the size of the inputs, the analysis can range from 10 minutes to 2 hours. |

|
|||||||||||||||
|
11
|
Retrieve KDA results. At the conclusion of KDA, key driver results files and cytoscape files are generated. The 'Key Drivers Results' file lists for each key driver its P and FDR values, the module of which it is a key driver for, the total number of neighbors ('N.neigh'), the number of neighbors that are members of the module ('N.obsrv'), and the expected (null) number of neighbors that are members of the module as calculated by permutation. The cytoscape files can be used on Cytoscape desktop for the user to customize the network visualization. Cytoscape visualization of the top 5 key drivers for each module can be viewed on the browser by clicking on 'Display KDA subnetwork'. The analysis can be concluded at this step or subnetwork genes can be used for drug repositioning in the PharmOmics pipeline by clicking on 'Run PharmOmics pipeline'. |

|
|
KDA Results Interpretation
|
|
Run KDA to PharmOmics |
|
12
|
(Optional) Select inputs for KDA to PharmOmics analysis. The user can conclude analysis at KDA or run drug based repositioning on KDA subnetwork results. Choose to run overlap (around 5 min to run) or network based drug repositioning (around 30 minutes to 2 hours to run). Next, choose all genes from the generated subnetwork, only genes from input modules (i.e. gene sets) in the subnetwork (not including subnetwork genes that are not members of input modules), or the user can choose specific modules to include. For drug network repositioning, you additionally need to select or upload a network and select the species. Also for network drug repositioning, we offer only the option to query meta signatures (studies using different dose and treatment durations are meta-analyzed). You may use your results in our separate PharmOmics pipeline to run the dose/time segregated analysis which will take around 3 hours to complete and will require a login due to heavy use of computational resources. |

|
|
13a
|
Retrieve PharmOmics results from overlap based drug repositioning. Image on the right shows results from the overlap based drug repositioning option. The results ranks the drugs based on concordance between the KDA subnetwork genes and the drug signatures genes (Jaccard score). Data from our comprehensive species- and tissue-specific drug signatures are used as well as L1000 signatures. The drug repositioning results and the genes used for repositioning can be obtained from the download links. |

|
|
13b
|
Retrieve PharmOmics results from network based drug repositioning. Image on the right shows results from the network based drug repositioning option. The results ranks the drugs based on the significance of connectivity between drug signature genes and input genes as defined by a gene network model. Signatures from our comprehensive species- and tissue-specific drug signatures database are used. The drug repositioning results and the genes used for repositioning can be obtained from the download links. We also provide links to visualize the network model of drug genes and their first neighbor input genes (input genes having one edge distance from drug gene). |

|
|
Run Meta-MSEA to PharmOmics |
|
14
|
Select input modules and drug repositioning type. Choose to run overlap (around 5 min to run) or network based drug repositioning (around 30 minutes to 2 hours to run). Next, choose to run all modules below a specified significance threshold or select specific modules. For drug network repositioning, you additionally need to select or upload a network and select the species. Also for network drug repositioning, we offer only the option to query meta signatures (studies using different dose and treatment durations are meta-analyzed). You may use your results in our separate PharmOmics pipeline to run the dose/time segregated analysis which will take around 3 hours to complete and will require a login due to heavy use of computational resources. Please refer to steps 11a and 11b to read interpretation of PharmOmics results. |

|
For a list of genes with no corresponding association values, there are a number of analyses that can be run to derive biological meaning. One can test whether this set or sets of genes are enriched for an GWAS, TWAS, PWAS, or EWAS study. One can also use this list of genes as input for key driver analysis to see whether these genes are enriched in neighbors of key regulatory genes. Click below to see a tutorial of the different options.
|
1
|
Start pipeline. Click on 'Weighted Key Driver Analysis'. |
|
||||||||||||
|
2
|
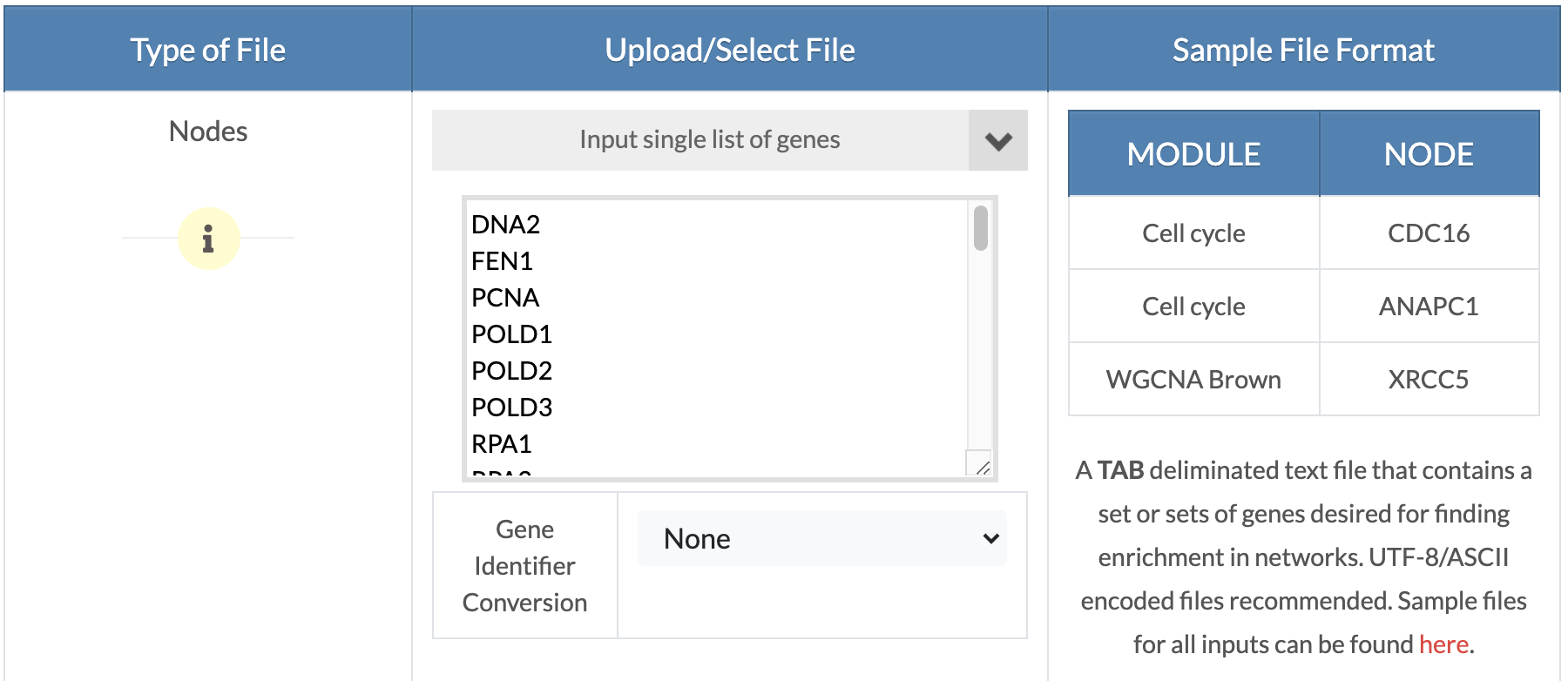
Upload OR copy and paste genes/nodes. From the 'Please select option' drop down menu, click on 'Upload Gene Sets' to upload a tab delimited gene sets file with a 'MODULE' 'NODE' header where the 'MODULE' denotes the gene set name and 'NODE' contains the corresponding genes. If you want to test just one gene list, the'MODULE' column can have a single arbitrary name or you can click on the 'Input single list of genes' option to drag and drop a text file or click to copy and paste a list of genes (shown on the picture on the right). In the next step, a gene sets description file can be uploaded. |
|
||||||||||||
|
3
|
Select/upload network file. The network file describes molecular connections. In a directed network, the source is in the 'HEAD' column and the target is in the 'TAIL' column. The network need not be directed or have weights (the 'WEIGHT' column can have all '1's). We provide sample tissue-specific gene regulatory networks and a protein-protein interaction network. |
File format
|
||||||||||||
|
4
|
Select parameters for key driver analysis. The search depth defines the distance (number of connections) away from a potential key driver that will be considered its local network neighborhood. A search depth of 1 is recommended. The edge type can be either 'Undirected' or 'Directed'; the former means that directionality (source and target designation) is not considered, and the latter means it is considered. The min overlap is the threshold above which hubs will be designated as co-hubs. The Edge factor is the degree of influence of a edge weight. 0 is no influence (all weights are equal)1 is full influence, and 0.5 is partial influence. |

|
||||||||||||
|
5
|
Review KDA files/parameters and submit job. Click 'Click to Review' to see files and parameters chosen. Click 'Run wKDA Pipeline' to submit the job. Depending on the size of the inputs, the analysis can range from 10 minutes to 2 hours. |

|
||||||||||||
|
6
|
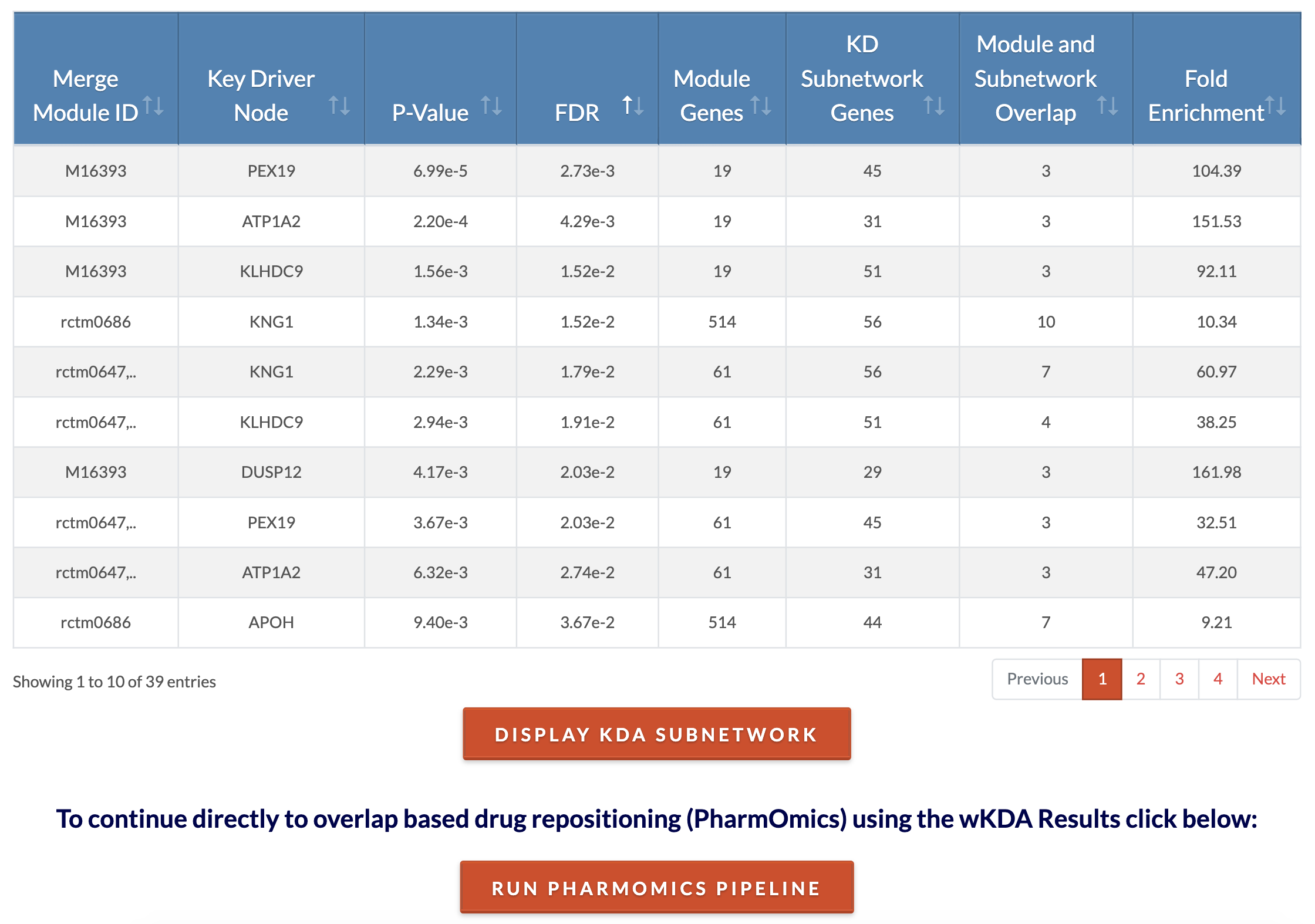
Retrieve KDA results. At the conclusion of KDA, key driver results files and cytoscape files are generated. The 'Key Drivers Results' file lists for each key driver its P and FDR values, the module of which it is a key driver for, the total number of neighbors ('N.neigh'), the number of neighbors that are members of the module ('N.obsrv'), and the expected (null) number of neighbors that are members of the module as calculated by permutation. The cytoscape files can be used on Cytoscape Desktop for the user to customize the network visualization. Cytoscape visualization of the top 5 key drivers for each module can be viewed on the browser by clicking on 'Display KDA subnetwork'. The analysis can be concluded at this step or subnetwork genes can be used for drug repositioning in the PharmOmics pipeline by clicking on 'Run PharmOmics pipeline'. In the interactive result table, the 'Merge Module ID' is the module name after merging redundant modules, 'Key Driver Node' is the key driver gene for the module, the 'P-value' is the enrichment p-value of the key driver gene's neighbors for module members, FDR is the false discovery rate for the enrichment value, 'Module Genes' is the total number of nodes in the gene module, 'KD Subnetwork Genes' is the total number of genes in the key driver subnetwork, 'Module and Subnetwork Overlap' is the number of key driver neighbors that are members of the module, and 'Fold Enrichment' is the enrichment of KD subnetwork genes within the gene module. |

|
|
1
|
Prepare gene sets file. Arrange your gene set(s) in a two column file with columns 'MODULE' and 'GENE'. If you have just a few gene sets or one gene set to test, it is advised to add them to a larger gene set list. You may download the sample canonical pathways (KEGG, Reactome, and BioCarta) from our resources page and add your geneset. The gene sets file format is shown on the right. |
File format
|
||||||||
|
2
|
Choose pipeline to test gene sets in MSEA. Choose pipeline of interest depending on which disease study (GWAS, EWAS/TWAS/PWAS/MWAS, or multiple studies) you would like to test for association of your gene set. We provide many example GWAS files. |

|
||||||||
|
3
|
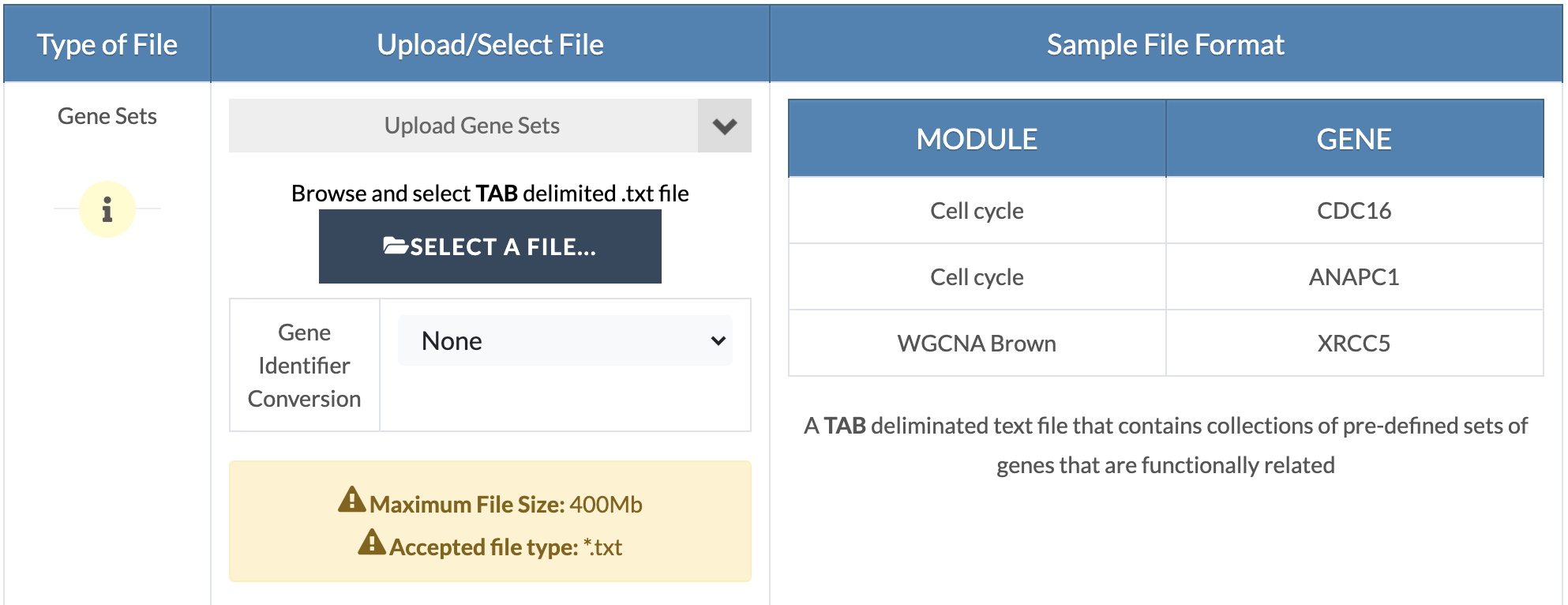
Upload gene sets. Upload your custom gene sets in the 'Marker Sets' input and select/upload remaining files and parameters (refer to embedded tutorials in the pipeline or the GWAS and EWAS/TWAS/PWAS/MWAS pipeline tutorials). |
|
||||||||
|
4
|
Retrieve MSEA results. In the MSEA results, you can see the degree of enrichment of your gene set(s). P-values, FDRs, and number of genes ('NGENES') from the association data contributed to the enrichment of the module are recorded. In the 'Module Details' file, the genes that contributed to the module's enrichment is recorded. |

|
All files are recommended to be in UTF-8/ASCII encoded format.
To see descriptions on how the pipeline can be used, click on the use cases below.
| Use case | Data | Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| 1. What are the genetic mechanisms of autism spectrum disorder (ASD)? What are the key regulators of those gene sets associated with ASD? What drugs can be used to target these disease networks? | GWAS | MDF MSEA KDA PharmOmics |
MDFGWAS summary statistics can be pulled from a study on ASD (detailing SNPs and their association values, i.e. p-values). The file format for input into MSEA is a two column tab delimited text file with two columns: 'MARKER' and 'VALUE'. SNPs occupy the 'MARKER' value and any measure of association strength can be put into the 'VALUE' column (most commonly used is -log10 transformed p-values but another measure such as effect size can be used). A higher value should indicate stronger association (hence -log10 transformed p-values). A recommended preprocessing step for GWAS is marker dependency filtering (MDF) which corrects for linkage disequilibrium. We offer the 1000 Genomes linkage files and will match the linkage population to the population that was tested in the GWAS (e.g. CEU is central europeans; the population codes can be accessed here). To enrich SNPs for gene sets, a SNP to gene mapping file is used such as expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs), and we choose to use brain tissue-specific eQTLs from GTEx. If running MDF, another parameter is to choose the percent top associations. We recommend 50% generally, but can be adjusted to 100% for small studies or 25% for large studies. If skipping MDF, the user will have to adjust the top percentage of associations to include before uploading their association data. MSEAAfter results are produced by MDF, we choose the inputs and parameters for MSEA. "Gene" based permutation is chosen to avoid bias from multiple markers mapping to the same gene (gene set could have high significance from a large amount of markers but those markers could map to just one gene). We may choose "marker" based permutation as an alternate, more lenient analysis. Since this is a an exploratory analysis, 1000 permutations are chosen and for formal analysis, 10000 number of permutations will be set which may take longer. Since we want to focus on the most significant pathways in the KDA, a MSEA to KDA export FDR cutoff of 5 is chosen (5% FDR). We leave the other parameters as the default values as this is recommended. More details of these parameters can be found above in the 'Parameters details' section. Finally, the marker sets (i.e. gene sets) chosen are the WGCNA and MEGENA coexpression modules for brain cortex made from GTEx expression data ('Brain Cortex Coexpression Modules'). In the results, enrichment P and FDR values are recorded for each gene set for genes mapped from SNPs. KDAFrom MSEA, we retrieve P and FDR values for each gene set. Modules from MSEA passing the FDR threshold to export results from MSEA to KDA will be undergo merging to combine potentially highly similar pathways and then be fed into wKDA. We leave most parameters to default values. Because we are using a dense network and have many genes (~500) as input into KDA, we leave the search depth to 1 to simplify the analysis and focus on more direct connections. We do not want to require the key driver to be upstream of the target gene, so we set the edge type to "Undirected". To have the edge weight to have partial influence on the analysis, we set edge weight to 0.5. We choose to run wKDA on a brain gene regulatory network on these significant modules. In the results, we identify key regulator genes of the modules based on network topology. A disease subnetwork is generated from the top 5 key drivers from each module (in the 'Cytoscape Edges' file). PharmOmicsIn the direct path from KDA to PharmOmics, the disease subnetwork genes can be used for overlap or network-based drug repositioning which can give gene network regulatory informed therapeutic insight into ASD. In overlap-based drug repositioning, the drugs are ranked based on the significance of the Jaccard score between the subnetwork genes and drug signature genes. In network-based drug repositioning, drugs are ranked based on the connectivity of their signature genes with the wKDA derived subnetworks as defined by a gene network model. Alternatively, if enough significant key drivers are identified, these key drivers can be used for drug repositioning. |
| 2. What functional gene sets are enriched for differentially expressed genes between high sucrose treated mice and untreated mice and do they overlap with type 2 diabetes GWAS? | TWAS, GWAS | Meta-MSEA |
|
For this aim, TWAS and GWAS data can be run in meta-MSEA. TWAS data can be the differentially expressed genes results obtained from comparing RNA-seq data from an insulin resistance mice model versus that of wild-type mice. The association file would have genes in the 'MARKER' column and the -log10 transformed p-values or absolute log fold change of expression in the 'VALUE' column (higher values indicate stronger association). Importantly, users should input the full association data, including the values that do not meet nominal significance. User can also trying including just the top 75%, 50%, and 25% of signals. Secondly, the summary statistics from a type 2 diabetes GWAS study and an association file for input into MSEA is prepared with SNPs in the 'MARKER' column and -log10 transformed p-value (or other association measure) in the 'VALUE' column. Since we are testing for enrichment of gene sets, SNPs will need to be mapped to genes whereas TWAS data do not need this further step. Please refer to the tutorial for further detail. In meta-MSEA, a meta enrichment for the pathways is calculated based on the individual GWAS and TWAS module results. With this analysis, we can boost the power to observe consistent pathways reflecting important biology across omics layers. The users should be mindful the individual enrichment values as well as the meta enrichment values. |
| 3. Which cell type specific differentially expressed genes (DEGs) of beta-amyloid aggregation mouse models are enriched for Alzheimer's disease GWAS? | Gene lists, GWAS | MSEA |
|
To answer this question, we can obtain cell type specific DEGs by performing single-cell RNA-seq mice with mutations causing rapid beta-amyloid aggregation and wild type mice and comparing the cell type gene expression levels. The DEGs for each cell type will be the gene sets for enrichment in MSEA (cell type in the 'MODULE' column and DEGs in the 'GENE' column). This gene set can be uploaded into the MSEA pipeline with summary statistics from an Alzheimer's disease (AD) GWAS study. Using this analysis, you can see which cell types may be important for AD pathogenesis. |
| 4. What genes are key regulators for protein folding genes in a brain gene regulatory network? | Single gene list | KDA |
|
A curated list of protein folding related genes can be used as input to KDA. The geneset list may have multiple sets designated in the 'MODULE' with corresponding genes in the 'NODE' column or just one set (the same value in the MODULE column). Or the genes can be directly input into a text field upon choosing the 'Input single list of genes' option. Key drivers found may be important regulators of protein folding. |
